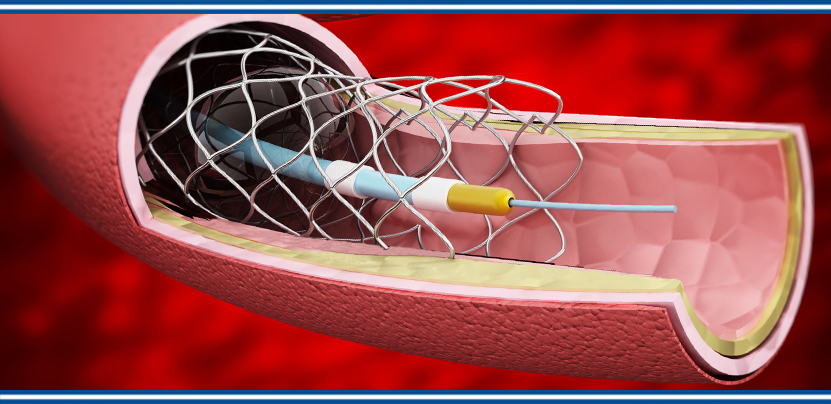
Angioplasty (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention - PCI):
Procedure: A catheter with a small balloon on its tip is inserted into a narrowed or blocked coronary
artery. The balloon is then inflated to widen the artery, allowing better blood flow.
Stenting: Often, a stent (a small mesh tube) is placed in the artery to keep it open after angioplasty.
Atherectomy:
Procedure: Involves the removal of plaque from arteries using a catheter with a rotating shaver or
laser. This technique is used for complex or calcified blockages that are difficult to treat with
angioplasty alone.
Thrombectomy:
Procedure: The removal of a blood clot from a blood vessel. This is crucial in acute heart attack
management to restore blood flow quickly and prevent extensive heart damage.
Valvuloplasty:
Procedure: A balloon catheter is used to dilate a stenotic (narrowed) heart valve. This is commonly
performed for conditions like aortic stenosis.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR):
Procedure: A minimally invasive surgery to replace a diseased aortic valve. The new valve is
delivered via catheter and expanded at the site of the diseased valve.
Percutaneous Valve Repair:
Procedure: Techniques such as the MitraClip are used to repair mitral valve regurgitation by
clipping the valve's leaflets together to reduce backflow of blood.
Cardiac Catheterization:
Procedure: Involves threading a catheter through the blood vessels to the heart. It is used to
diagnose and treat various heart conditions, including measuring pressures in the heart chambers and
injecting contrast dye for imaging.